By Sean M O’Brien
Up until now, peer review has been held up as the gold standard in scientific discourse. Recent developments in the climate science arena, such as Climategate, have led many to conclude that peer review is not all that it is cracked up to be. Having said that, peer review may well be perfectly adequate as a scientific standard when the issues in debate are the mating habits of squirrels. However, if the issue in debate is whether or not trillions of dollars should be spent combating global warming, perhaps a new more rigorous standard should be applied.
I propose that henceforth, five levels of scientific rigour be defined. In brief, they are Level zero which is grey literature from advocacy organisations such as the WWF. Level one, which is the current peer review process. Level two, which I will call replicatable, is the current peer review process but with mandatory archiving of data and software code within six months of publication. Level three, which I will call audited, is where an authoritative body of some sort holds a competition on the internet to “find something wrong” with the calculations in the paper with a prize for any independent researcher who can find incorrect calculations. Level four is what I will call Cross Examined and is where the paper in question is deemed so important that, a full scale “internet trial” is conducted. You can think of it as a Scopes Monkey Trial of the researchers and their paper by competent legal personnel advised by scientists. It would mainly consist of oral testimony but with anyone on the internet free to comment and interject in any forum they wish. Naturally these comments can inform the questions put to the researchers.
The main effect of this idea would be to shift the public debate to a new level. Instead of the phrase “the science is peer reviewed” being used to silence sceptics, the phrase “the science is only at level 1” would be used to prompt debate.
What is needed to give this idea teeth is a law. Let us call it the Scientific Integrity Act. Let me focus the discussion from here forward on the United States as most people from around the world will be familiar with how the process of government operates there. The key thing about the Scientific Integrity act is that it should place a limit of the amount of government spending and / or related industry and consumer costs, that can be legislated for based on the level at which the science is at. To take an example. Level 1 science, would not be allowed to justify any government spending or imposed costs. Level two science might perhaps justify $10 million dollars of government spend and $50 million of imposed costs and so on. Needless to say, any proposal with trillion dollar price tags would need level four science to justify it.
Another facet of the law would be that researchers in receipt of a federal grant have to designate their research paper as being at a particular level. In order to encourage realistic assessments of papers by their authors, a penalty system would be included that would operate like this. If a researcher designates their paper as a level three, then should an independent researcher find something wrong with the maths, the funding agency who funded the study would pay a fee to the independent researcher. The fee would be the equivalent of the cost of producing the paper. Naturally a funding agency that got hit as a result of the sloppy mathematics of a researcher would be less likely to fund more bad science by the researcher.
So the big question is of course how would level four scientific papers be selected. I see it working like this. Any government agencies, or legislators, that wish to propose laws based on science, have to nominate ten scientific papers to be assessed at level 4. One would hope they would pick the ten best papers, but just in case, there would be a provision for a minority of legislators in the relevant legislature to substitute five of them. IE if the majority in a 100 seat legislature propose some legislation and nominate 10 papers, then a grouping of 20 legislators would have the right to substitute five of them for other papers.
I would not see anyone sitting in judgment on level four papers. Remember in order to get to Level four, they will already have been audited at Level three so the math will be correct or at least defensible. Rather I would see questioning both orally and via written submissions of researchers as to why they made particular decisions and interpretations. This information would then be available on the web to anyone and the preponderance of scientific opinion and comment would influence legislators to vote for or against the legislation.
Let us consider a hypothetical example. Supposing a researcher decided to use a non-standard mathematical technique that had the effect of producing a particular shape for plotted data even if random number were fed into it. Then, if the researcher tried to defend this notion on the stand, one would expect that the legal teams questioning him would expose this and that the legislators would spot this for what it was. (Then again, one would hope that the paper in question would not have made it past level three in any case.)
Some people, especially AGW believers, may view this proposal as being expensive, both in terms of cost and in that it would delay much needed action. I would maintain the opposite. Currently billions are being spent to persuade an increasingly sceptical public that the world is about to fry and despite the billions, legislative attempts to curb carbon emissions have stalled in most countries across the world. The cheapest and fastest way to get action would be to simply put the top ten research papers that prove the AGW hypothesis through a level four Scopes Monkey type trial.
If the science emerges unscathed from this process, then I for one can see myself persuaded. I suspect that many other sceptics, as opposed to contrarians, would similarly be persuaded. So let us issue the challenge to the AGW community. Name your top ten papers and let’s put them on trial.
With regard to how to progress this idea, I would suggest three things.
Firstly, someone or somebody should do an audit of all the scientific papers referenced in the IPCC reports to see if they are at level one or two. Level two remember is where the data and code is released within six months of the publication of the paper. Perhaps a project similar to Surfacestations.org might be the way to go. Given what I read on the various sceptic climate blogs, I suspect that little enough of the science would make it to level two. As an aside, Donna LaFramboise already did a similar audit looking for grey literature references across one of the IPCC reports and found that 35% of the references were level zero. Imagine the change in discourse if one could confidently say that most of the science in IPCC 4 is level zero or one.
Secondly shift the debate. When discussing the issue with friends or in the media, explain the levels and ask them would they think it reasonable that the science behind a measure that will cost billions should be subject to a certain amount of scrutiny.
And finally, all those Republican controlled state legislatures across America should put forward a Scientific Integrity act in their state. Given the power balance federally there would be no point in introducing the act federally at this time. However, a couple of state legislatures enacting a Scientific Integrity bill would put huge pressure on the AGW community to nominate the top ten papers and put them on trial. More. H/T GWPC
By Dr. Tim Ball
In an article which appeared in last Sunday’s Sacramento Bee paper, among other propaganda, was this assertion, by “Pacific Council on International Policy’s Climate Change Adaptation Task Force”:
“Scientists, for example, have only recently been able to measure with certainty what has long been more generally known - that the Arctic ice cap was dramatically declining. The thickness of that ice turns out to have shrunk 50 percent during the past 50 years.” (H/T L.Cenatto)
It is correct that we have only had reasonably accurate measures of the ice area since 1980. The satellite went up in 1978 but the first two years of data are unreliable as they worked to establish procedures and determine accuracy. Since then various computer models have used different methods to measure and display what is going on. There is still disagreement. Ice thickness was never a measure of the satellite, although they have tried to distinguish between old, young and new ice.
The argument about thinning is rubbish and based on the original ice thickness measurements taken by USS Sargo traversed under the ice in 1960. It followed the surfacing at the North Pole by USS Nautilus the first nuclear submarine in 1958.
The interest and experiments were driven by the discovery that Soviet submarines were getting into the North Atlantic by transiting under the ice and then passing through the deepest channel out of the Arctic Basin, the East Greenland Channel, thus bypassing the submarine and air barrier set up between Iceland and Scotland. Ironically we now have access to the Russia material but nobody pays much attention, but that has been the course of the climate debate all along (here).
An early assessment of the situation was produced by Fritz Koerner.
In 1999, a second transit measured ice thickness again using US submarines. As usual the New York Times was stoking the warming fires.
“The research involved measurements of sea ice thickness made by upward-looking sonar aboard naval submarines operating under the ice sheet. The first period of data began in 1958 with the first nuclear submarine, the United States’ Nautilus, and concluded with a cruise by H.M.S. Sovereign in 1976. The second data set was collected by American vessels from 1993 to 1997. Dr. Rothrock and two colleagues, Y. Yu and G. A. Maykut of the University of Washington, compared data from the two periods at 29 points where the courses of submarines in the 1990’s intersected with the courses of those in the earlier period.”
This became the main source of the thinning scare. The problems with the research include;
1. The submarines did not follow the same route.
2. The used different measuring equipment; one was a sideways scanning system that determined the bottom of the ice and then they estimated the thickness. The other was a vertical system that determined thickness in a different way.
3. The transits were made in different months and Arctic ice changes are naturally dramatic from month to month. For example, some 65,000 km of ice melts or forms daily.
4. Ice thickness is not just due to atmospheric temperatures but determined by water temperatures among other factors. One of these is the weight of the ice which varies with snowfall that pushes the ice down into the ocean so it melts. The ice thickness is limited by this and the only way you get substantially thicker ice is when the slabs of ice collide and cause massive ridges.
5. The winters in 1960 were naturally much colder and snowier than in 1999 and the warming was not due to CO2 but increased solar activity..
Following the US transits the British Navy did some measures in 2004.
By then the impact of ocean currents and transport of warmer water into and under the ice was being officially acknowledged (here and here).
Of course none of what is going on today is outside long term variation in ice cover. Consider the report from the Royal Society to the Admiralty in 1817.
Ice melting and thinning are more of the out of context exploitation of people’s fears and lack of knowledge or understanding. (Icecap Note: Tamino included)
See post here. Note: expanded story coming in the Canada Free Press soon.
See this analysis by the International Arctic Research Center.
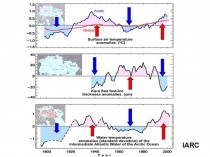
See enlarged here.
By Dan Vergano, USA TODAY
The author of a report critical of climate scientists defended himself against plagiarism charges Tuesday, and denied he was pressured by Republicans to tilt the report.
Offered the chance to further respond to plagiarism allegations, reported Monday in USA TODAY, George Mason University statistician Edward Wegman said in an e-mail that “these attacks are unprecedented in my 42 years as an academic and scholar.”
Wegman was the lead author of a 2006 congressional climate science report that has become central in the debate over whether findings of global warming are warranted by scientific evidence.
BACKGROUND: Experts claim 2006 climate report plagiarized
Three plagiarism experts contacted by the newspaper said excerpts in the Wegman report were likely plagiarized from various sources.
The charges first surfaced on the Deep Climate website in 2009 and later in an analysis by retired computer scientist John Mashey of Portola Valley, Calif.
GMU spokesman Dan Walsch said in an e-mail that the university is investigating the matter.
“I will say that there is a lot of speculation and conspiracy theory in John Mashey’s analysis which is simply not true,” Wegman said.
“We are not the bad guys… We have never intended that our Congressional testimony was intended to take intellectual credit” for other scholars’ work.
Wegman said he and his report co-authors felt “some pressure” from a House committee to complete the report “faster than we might like.” But he denied that there was any attempt to tilt the influential climate report politically.
He said the committee “wanted our opinion as to the correctness of the mathematics” used in two climate studies.
“They wanted the truth as we saw it,” Wegman said.
Read more here.
By Joanne Nova
Ad Hominem Unleashed: On the origin of the sceptics
Commentators on a sinking ship search for reasons to “keep the faith afloat”.
The battle cry: the “skeptics” are shills of big oil, has become an own goal. The PR team for the catastrophic theory have no new evidence of Big Oil funding and thousands of people now point out that the UNskeptics were paid 3500 times as much (at least). So they are moving on...the religiously devout believers can’t admit they were wrong, and nor can they look at the evidence, so what’s left? Post hoc random over-analysis of the irrelevant. Before, skeptics were paid hacks...and now they’re wrong because they… are ideologically against big government and regulation. From one ad hom to another.
And again, the ABC uses our taxes to promote the smear campaign, support neolithic reasoning, and does everything it can to stop people talking about scientific evidence (by spreading misinformation or slurs about all the characters on one side). Oreskes and freelance writer Graham Readfearn can’t discuss the evidence (or lack of) for their favourite faith, but they spend a lot of time digging up irrelevant details instead.
Are man-made emissions a problem? How would we find the answer? Look not at sedimentary rocks but at stationery and submissions. As if the answer to tropical convective processes might be hidden on IPA letterhead, or in subliminal messages coded in the number of peer reviewed reports. It’s tea-leaves and rune-stones stuff, and people kid themselves that Blackberries or Androids make us modern, but the writing of people like Oreskes and Readfearn reminds us that human brains still carry software from the paleolithic. They simply can’t string a reasoned scientific argument together without resorting to discussing motivations, character, ideology or gossip about who their friends are.

Here’s Oreskes. She “knows” she’s right, she just has to figure why other people haven’t seen the light too:
“It’s part of this whole ideological program of challenging any science that could lead to government regulation, because it’s part of an ideological conviction that all regulation is bad, that any time the government steps in to ‘protect’ us from harm, that we’re on the slippery slope to socialism, and this is the ideology that you see underlying a kind of almost paranoid anti-communism. So even after the Cold War is over, these people are seeing reds under the bed.”
Ponder the inanity of “paranoid anti-communism?”
The Death Toll from far-left governments has been tagged at more than 100 million which is about three times higher than the current known death toll from AIDS. You can see how meaningless the Oreskes line-of-wordsmithing becomes. What’s the difference: paranoid anti-communism, or paranoid anti-AIDSism?
The difference is, Oreskes won’t be trying to inanely badge or label the AIDS workers.
What is left to describe as a rational fear if being afraid of mass murder is “paranoid”?
The double fallacy: When the ad hom isn’t even correct
Evidence matters so little to the smear campaigners that Readfearn doesn’t even bother to research his ad hominem targets:
You can’t help but think that Roskam must have been chuckling to himself as he wrote that statement, given the paucity of actual peer-reviewed scientific research on climate change amongst the book’s contributors, which included Ian Plimer, Richard Lindzen, Nigel Lawson, William Kininmonth, Willie Soon, Christopher Monckton, Garth Paltridge plus the IPA’s own Alan Moran and Roskam himself.
Thus, hundreds of peer reviewed papers are described as a paucity. Richard Lindzen: 235 peer reviewed papers. Garth Paltridge: scores (in journals like Nature, J. Geophys. Res., J. Atmos. Sci., Q. J. Roy.Meteor. Soc), Willie Soon: dozens (Like Climate Research, Energy & Environment, and The Astrophysical Journal).
Ten minutes to google and Readfearn couldn’t be bothered. He apparently wants everyone to think that only people with peer reviewed climate papers should be listened too, but while he thinks climate scientists with hundreds of papers are worth mocking, he’s proud of his own climate science record. His opinions on the climate are worth televising. (According to him, and, of course, the ABC):
Earlier this year, Lord Monckton was featured heavily in newspaper coverage when he conducted a speaking tour in towns and cities across the country, including a debate in Brisbane which was televised by the ABC (featuring yours truly). Monckton, like the majority of sceptics, has no science training and while he is undoubtedly one of the highest-profile sceptics, he has never had a peer-reviewed climate science paper published. And Readfearn of course has not published a peer reviewed paper either. But he’s a journalist. Again, one of the anointed for whom the laws of logic part like the Red Sea.
On the plus side though, Readfearn is flexible - it’s not just ad hominem attacks and argument from authority - he can do other logical fallacies too. When he needs to, he can confuse cause and effect:
At one point or another, pretty much every one of these climate sceptics (or sceptics of the need for action) have also been hosted by one or more of the US-based free-market think-tanks.
He think the “links” are meaningful as if correlation was causation.
The free market think tanks - shock me - approach people who have also come to similar conclusions. And passionate scientists not-so-surprisingly seek out groups and conferences of like-minded people.
Though as it happens the dastardly think tanks also approached Al Gore. The only difference is that Al was too scared to speak at one of the free market think tank events, even if they paid him. He knows he can’t answer their questions.
Oreskes and Readfearn’s ability to reason is so confused they can’t think their way out of a paragraph. You know you’ve found another taxpayer funded cesspit of reason when the writers can’t even pass their own flawed “tests”.
As I wrote before, Oreskes IS the Merchant of Doubt, and she speaks today (Monday in Perth at 6pm at UWA).
See post here.
By John O’Sullivan Live Journal
Angry pro-green biologist suspected of fraud ejects TV producer from university interview to evade probing questions over hidden data.
Australian biologist, Roslyn Gleadow of Monash University, Melbourne raised eyebrows recently in her much trumpeted alarmist paper, ‘Growth and nutritive value of cassava are reduced when grown in elevated CO2’. Now she deepens suspicions of wrongdoing by storming out of a media interview.
Science of Carbon Dioxide on Plant Growth Re-written?
These new “findings” widely hyped on pro-green news outlets have come under closer scrutiny since discredited Climategate crank, Kevin Trenberth (see video here) rushed to the authors’ defense. Bizarrely the controversial study totally contradicts the findings of a large body of science that has told us for years that carbon dioxide (CO2) is an essential plant food and adding more of it increases organic growth.
Moreover, it is established practice in agriculture that enclosures using increased CO2 promote crop yields, is good for agro-business and consumers as it leads to increased efficiency and cheaper food prices.
But, as we shall see below, when the Aussie biologist was asked during an interview to explain why her conclusions contradicted the findings of such eminent scientists such as Katsu Imai (1984) and others, she dramatically ended proceedings.
Gleadow’s freakish behavior is set to fuel further speculation that she and the paper’s co-authors, John R. Evans, Stephanie McCaffery and Timothy R. Cavagnaro are complicit in another high-profile eco-fraud.
Angry Green Researcher Refuses to Explain Anomalies
Key to this issue is the very crop this latest study examined: cassava. It has long been held that the original 1984 peer-reviewed evidence proved CO2 increases cassava root yields. However, this latest alarmist study somehow points to a decrease in such yields.
But when Timothy Wells, a free-lance TV producer and interviewer sought to persuade Gleadow to answer detailed questions on this headline-grabbing story she turned nasty. Gleadow became evasive and wouldn’t give a straight answer to explain her extraordinary conclusions; clearly not demonstrating the accepted standards of transparency and integrity expected in the wider scientific community.
From the moment it was published independent experts have questioned how this Aussie paper that even cites the widely established prior paper by Kimball (1983) could so dramatically contradicted those earlier results.
Kimball had analyzed 430 prior observations on the effects of CO2 enrichment and have demonstrated a consistent average increase of yield to 33% from a doubling of CO2 - a startling contrast to the 80% DECREASE claimed by Gleadow et al.
Security Called to Eject Interviewer From University
On a wave of pro-green media interest and to ramp up the hype on her study Gleadow agreed to be interviewed by Wells. The interview took place on November 12, 2010 at Monash University, Melbourne. Upon their meeting Wells found Gleadow’s zealotry typifying all that the public has grown to expect from pro-green activists. She was soon into her stride emphasizing that “unless Co2 emissions are dramatically reduced...there could be severe food shortages.”
But when Gleadows realized Wells wasn’t one of the usual servile mainstream news media journalists that pander to such greenwash things turned ugly. Wells reports, “When I mentioned ‘yield’ [she] promptly said that permission for the interview was now withdrawn and that I was to leave the office.”
Wells adds, “Many excuses were offered” which he wasn’t buying. Gleadows became irate and Wells recalls, “security was then called but I left before any problem arose.” The episode left a bitter taste in the mouth with Wells pondering the question: “What does this scientist have to hide?”
Well-funded Greenwash Conspiracy Uncovered?
Not to be outdone, Wells looked again at this paper that’s supposedly about plant growth and noted that the researchers mention the phrase ‘climate change’ no less than 14 times. It was at this point he began to ponder whether there may be an deeper unseen motive there for fraud.
Wells then discovered that the source for the paper’s funding had been the Finkel Foundation. This organization is the brainchild of Dr. Alan Finkel who also finances a far left environmentalist magazine called “G.” Sat on the advisory board of “G” is Tim Flannery, Sir Richard Branson and several other staunch climate doomsaying activists with deep pockets.
But even more pointedly, Dr. Finkel was the Chancellor of Monash University at the time this “research” was done. We may not yet have a full-blown ‘Cassava-gate’ but expect to read much more on this story as the plot thickens.
Reference:
Gleadow, R., Evans J. R., McCaffery S., & Cavagnaro, T. R., ‘Growth and nutritive value of cassava (Manihot esculenta Cranz.) are reduced when grown in elevated CO2’, (June 22, 2009), German Botanical Society and The Royal Botanical Society of the Netherlands.
By Steven Goddard
The raw data shows a strong cooling trend for maximum temperatures in Liberty, Texas.

Through the magic of USHCN adjustments, this cooling trend gets turned into a warming trend.

The graph below shows the adjusted data overlaid, and normalised to 1910. Note that they have added an impressive four degrees to the trend!

I find this nothing short of incredible.
See post here.
UNU’s Institute for Environment and Human Security (UNU-EHS)
Amid predictions that by 2010 the world will need to cope with as many as 50 million people escaping the effects of creeping environmental deterioration, United Nations University experts say the international community urgently needs to define, recognize and extend support to this new category of ‘refugee’.
In a statement to mark the UN Day for Disaster Reduction (October 12), UNU’s Institute for Environment and Human Security (UNU-EHS) in Bonn says such problems as sea level rise, expanding deserts and catastrophic weather-induced flooding have already contributed to large permanent migrations and could eventually displace hundreds of millions.
Unlike victims of political upheaval or violence, however, who have access through governments and international organizations to such assistance as financial grants, food, tools, shelter, schools and clinics, “environmental refugees” are not yet recognized in world conventions.
UNU says the number of people forced to move by environment-related conditions already approximates and may someday dwarf the number of officially-recognized “persons of concern,” recently calculated at 19.2 million1. Indeed, Red Cross research shows more people are now displaced by environmental disasters than war.
“There are well-founded fears that the number of people fleeing untenable environmental conditions may grow exponentially as the world experiences the effects of climate change and other phenomena,” says UNU-EHS Director Janos Bogardi. “This new category of ‘refugee’ needs to find a place in international agreements. We need to better anticipate support requirements, similar to those of people fleeing other unviable situations.”
Victims of sudden and highly-publicized catastrophes like the 2004 Asian tsunami or the recent US Gulf Coast hurricanes benefit from the mobilization of private and public sector generosity and humanitarian relief. Countless millions of others around the world, however, are uprooted by gradual environmental change, receive comparatively little support to cope and adapt and are not recognized as ‘refugees’ with the benefits that bestows.
“This is a highly complex issue, with global organizations already overwhelmed by the demands of conventionally-recognized refugees, as originally defined in 1951. We should prepare now, however, to define, accept and accommodate this new breed of ‘refugee’ within international frameworks,” says UN Under Secretary-General Hans van Ginkel, Rector of UNU.
Prof. van Ginkel stresses that environment-related ‘refugees’ must be carefully defined and distinguished from economic migrants, who depart voluntarily to find a better life but may return home without persecution.
Dr. Bogardi notes that the term “environmental refugee” rankles many experts as simplistic, masking what are often compound motives behind migration and implicitly laying the blame on nature when often the policies and practices of people are the cause of displacement. UNU-EHS is working to establish an internationally-agreed glossary of terms to facilitate cooperation in the broad area of environment and human security.
As well, most such displaced people today migrate within their own country. There is therefore a major need for international agreement about a nation’s duty to protect and support internal migrants fleeing catastrophic events or environmental degradation. That duty is implied in the agreement produced by the World Conference on Disaster Reduction in Kobe, Japan (Jan. 2005) and international guidelines on internal displacement have been promoted. However, states’ obligations need to be formalized, says Dr. Bogardi.
The statement coincides with the announcement of a new chair on social vulnerability at UNU-EHS, funded by a charitable foundation of the global reinsurance company Munich Re. Among the areas of study will be migrations forced by “slow moving catastrophes,” says Dr. Bogardi, including desertification, diminishing safe water supplies and climate change-induced sea level rise.
Environment-related migration has been most acute in Sub-Saharan Africa, but also affects millions of people in Asia and India. Meanwhile, Europe and the United States are witnessing increasing pressure from victims of often mismanaged and deteriorating soil and water conditions in North Africa and Latin America.
And such migrations may grow dramatically in future.
Among many global problem sites, Sana’a, Yemen’s capital, has doubled its population on average every six years since 1972 and now stands at 900,000. The aquifer on which the city depends is falling by 6 meters a year, and may be exhausted by 2010, according to the World Bank.
In China, the Gobi desert expands more than 10,000 square kilometers per year, threatening many villages. Oxford-based expert Norman Myers says Morocco, Tunisia and Libya each lose over 1,000 square kilometres of productive land a year to desertification. In Egypt, half of irrigated croplands suffer from salinization while in Turkey 160,000 square kilometres of farmlands is affected by soil erosion.
Florida professor Tony Oliver-Smith is a UNU-EHS Munich Re Foundation chair holder designate for 2007-08, whose work will include study of the recent exodus from New Orleans and other environment-related migrations. He notes that in the U.S. Louisiana now loses to the sea roughly 65 square kilometers per year while in Alaska 213 communities are threatened by tides that creep roughly 3 metres further inland each year.
Internationally, the low-lying Pacific island state of Tuvalu has struck an agreement with New Zealand to accept its 11,600 citizens in the event rising sea levels swamp the country. By one rough estimate, as many as 100 million people worldwide live in areas below sea level and / or are subject to storm surge.
“Around the world vulnerability is on the increase due to the rapid development of megacities in coastal areas,” says Dr. Oliver-Smith. “Many cities are overwhelmed, incapable of handling with any degree of effectiveness the demands of a burgeoning number of people, many of whom take up shelter in flimsy shanties.
“Combine this trend with rising sea levels and the growing number and intensity of storms and it is the recipe for a disaster-in-waiting, with enormous potential to create waves of environment-driven migration.” He says it is difficult today to discern “environmental refugees” from economic migrants. In many cases a decision to move is a function of a push to leave one disaster-affected location and the economic pull of another, more promising location. American history offers vivid examples: the 3 million people who fled the Dust Bowl of the 1930’s and the 700,000 mostly poor people who departed to northern states following the Mississippi Delta flood of 1927.
Read more here. Another failed UN forecast. H/T Marc Morano.
Marc Hendrickx
ABC Unleashed’s favourite psychologist Stephan Lewandowsky once again takes aim at those suggesting it might be prudent to wait for the facts to come in, before turning society on its head. All to combat a climate crisis that has been manufactured up by activists with a poor appreciation of what constitutes a hazard; generally inner city folk.
This time round in a piece titled “Climate change: are you willing to take the risk?” Lewandowsky suggests the level of certainty in climate science is similar to other well founded scientific principles like gravity. He contends that if climate science has the same veracity as evolution for example, who wouldn’t be prepared to sell their children and prepare for climate Armageddon? However, if we apply the same level of uncertainty inherent in climate science concepts to other disciplines it seems there is little to justify Lewandowsky’s level of confidence.
If IPCC Climate scientists were Physicists: The IPCC has found that the total net anthropogenic forcing is 1.6 W.m-2 with an error range of 0.6 to 2.4 W.m-2. If the IPCC’s same errors for Radiative Forcing Components were applied to the universal gravitational constant, IPCC climate scientists would tell us that the UGC is 6.67 × 10-11 N·m2/kg2 with a range of 2.5-10 N·m2/kg2. They would then assure us there is 90% certainty that acceleration due to gravity on Earth at sea level is in the range 3.7 to 14.7 m.s-2. IPCC climate scientists would tell us apples may be as light as a feather or as heavy as a brick. They would tell us apples fall down, but they’d be unable to tell us how fast, and occasionally they may actually fall upwards. As a result of their endeavours, Newtonian physics and Relativity would be tossed on its head. Quantum physics, built on the uncertainty principal, would have no place in a world where the science is settled. Speaking about gravity IPCC climate scientists would say things like: “The fact is that we can’t account for the lack of gravity at the moment and it is a travesty that we can’t.” They would earnestly explain that there was no statistically significant gravity from 1995, and suggest that anyone disagreeing with their assessment must be a gravity denier.
If IPCC Climate Scientists were engineers: If IPCC climate scientists were engineers they wouldn’t use rulers to measure distance, they’d use the wind. IPCC climate models predict a hot-spot over the tropics but thermometers attached to weather balloons show no sign of it, the hotspot is missing. So with no warming in the thermometers IPCC climate modelers looked elsewhere and claimed to have found it in wind shear. Throw away your calculators, they would tell the engineers the answer is blowing in the wind. So how would IPCC climate scientists go at engineering? Early attempts at engineering by IPCC climate scientists are documented in the image to accompany this piece above; the effect of wind shear not accounted for in this case: Would you trust an IPCC climate scientist to build your building?
If IPCC Climate scientists were laser eye surgeons. In a report titled “Draft Water Sharing Plan Greater Metropolitan Region unregulated river water sources.”, the NSW Office of Water has forecast rainfall and runoff across NSW using 15 global climate models for the IPCC SRES A1B climate scenario; finding:
For the Greater Metropolitan Region the worst case forecast is a 5-10 per cent reduction in mean annual rainfall by 2030, while the best case is a 5-10 per cent increase in mean annual rainfall. 7 of 15 models predict that mean annual rainfall would decrease by between 2 and 10 per cent, while 8 of 15 models predict that rainfall would increase by between 2 and 10 per cent by 2030.
Half of these models are wrong! What other science happily promotes incorrect models and expects politicians to make decisions based on spurious outputs? And Lewandowsky suggests that IPCC climate science has the same precision as laser surgery!
Applying the same laser like precision of the climate models to eye surgery in 7 out of 15 cases IPCC climate scientists as laser surgeons would blind the left eye, while in 8 out of 15 cases they would blind the right.
If IPCC climate scientists were historians. The palaeo-temperature study that gave the world the Hockey Stick Graph has now been debunked so many times that even the Australian Academy of Sciences concedes the existence of the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age. Based on the mess they made of the last 1000 years of climate, if IPCC climate scientists were historians they’d find no evidence for the French and Russian Revolutions. Copernicus, Galileo and Einstein would be cast into the dustbin denounced as deniers of prevailing authority. They would ignore Napoleon’s defeat in Russia because the weather could never have been so cold in the 19th century. There’d be no Renaissance, the authorities would not allow it. Aristotelian philosophy would rule supreme over the scientific method. If IPCC climate scientists were historians, history would only record those events officially sanctioned by governments, queen and kings. Only those facts that supported the prevailing view would be recorded for posterity; inconvenient truths have no place in the official accounts. Thankfully IPCC climate scientists are hopeless at history.
If IPCC Climate scientists were climate scientists: With current warming trends at about 0.1 degrees C per decade, well short of the warming required to lend credence to IPCC climate models that forecast rates of 0.3 to 0.7 degrees C per decade it seems climate scientists are not even capable of doing their own job let alone anyone else’s.
And if IPCC climate scientists were fruit pickers: they would obviously pick the cherry. They appear so used to cherry picking data to fit the models there simply is no other fruit, except perhaps the Durian, which is a nice metaphor for the current state of the IPCC.
IPCC science: are you willing to take the risk?
Marc Hendrickx works as a part time consulting geologist and is completing a PhD at Newcastle University.




