Jan 08, 2011
How can climate scientists spend so much money?
Climate Quotes
ICECAP NOTE: One of the certain brain-dead, knee-jerk reactions in comments to any posted article with any semblence of balance or skepticism on greenhouse global warming is that “big oil” must be funding the author or the skeptics. Nothing could be further from the truth. Exxon was accused of funding alternative thinking on climate change to the tune of $22 million the last few decades (most of the before 2000). No mention that Exxon gave $100million to Stanford and BP $500 million to the University of California Berkeley. Exxon and most big oil companies have gone green. There is also no recognition that the government funds climate change research - read global warming - to the tune of $2.3 billion to further their social agenda as this excellent expose shows below. That is a place for the congress to look to save money. The remaining research sollars should be to study climate change not global warming because there is a very real possibility that due to the sun and oceans, a major global cooling could take place and very little research dollars focus on this.
How can climate scientists spend so much money?

US Federal government spending on climate change research in 2011 (enlarged here).
Until a few days ago I knew that the US government spent an excessive amount of taxpayer money on climate change research. It was just a general notion; I had read occasional articles showing the funding of certain agencies like NASA but I didn’t know many specifics. Then on New Years Day, I wrote a very quick article where I randomly picked a document from a Google search showing funding for climate change. The numbers astonished me. I decided to take a closer look.
The document is the The American Association for the Advancement of Science’s report: AAAS REPORT XXXV, RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT FY 2011
The entire report is here, but I am only looking at chapter 15 which is here. Icecap Note: See how the AMS has authored this chapter. The report is basically a snapshot of US Federal spending on research, including budgets for 2011 and how these numbers compare to previous years. The chapter on climate change is short and easy to read. It shows that all US agencies that conduct climate change research are expected to have larger budgets for 2011. Remember, these numbers are not set in stone, but they will not be drastically different from the actual numbers. I also need to make a caveat. Just because this funding has been labeled ‘climate change research’ does not mean it is necessarily not linked to another field as well. For example, some of the costs associated are for satellites, which are important in more than just climate research. This is not entirely frivolous spending. Even so, the numbers are staggering. Let’s look at some agencies and their budgets.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
NOAA’s total budget request is $5.6 billion, which would be an increase of 17.0 percent. Of this, $437 million would be for climate research funding, which is an increase of $77 million.
$437 million spent on climate change research in one year, in one agency. Here’s another:
National Science Foundation (NSF). NSF would receive $7.4 billion in FY 2011, an increase of 8 percent relative to the FY 2010 appropriation. The request includes $370 million under the USGCRP framework, which is an increase of 16.0 percent. The Geosciences Directorate would receive $955 million (a 7.4 percent increase) in FY 2011 with $480 million going to Atmospheric and Earth Sciences. NSF’s Science, Engineering, and Education for Sustainability (SEES) program would receive $765.5 million. This is intended to promote discoveries and capability needed to inform societal actions in ways that contribute to environmental and economic sustainability. NSF’s request also includes $19 million for RE-ENERGYSE, a joint program with the Department of Energy intended to promote education in clean energy research. An additional $10 million would fund Climate Change Education, which seeks to increase understanding of climate among the next generation of Americans.
$480 million here, $765.5 million there, throw in another $10 million for climate education and you’ve got $1.25 billion dollars spent on climate change research just at the NSF, just in ONE YEAR! Next is NASA:
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). NASA’s FY 2011 budget request is $19.0 billion. NASA Earth Science is a relatively small fraction of this total, $1.8 billion or 9.5 percent, but would increase substantially relative to the FY 2010 appropriation (up 26.8 percent). NASA Earth Science funds climate change R&D through several programs. Two of particular note are Earth Science Research, which would receive $438.1 million (an increase of 14 percent)…
It seems like the $450 million mark is a common budget for climate research among these agencies. NOAA’s funding, the NSF’s atmospheric science funding, and NASA’s Earth Science research are all around $450 million. It may be an interesting coincidence. Next is the Department of Energy:
Department of Energy (DOE).
The President’s budget request for DOE in FY 2011 is $28.4 billion. This includes $4.6 billion for R&D in the Office of Science (an increase of 3.8 percent), and $2.4 billion for energy R&D (an increase of 6.8 percent). Within the Office of Science, the Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER), which supports basic research in atmospheric sciences, terrestrial ecosystems and climate modeling, would receive $627 million (an increase of 3.8 percent). BER’s request includes $28.6 million for the Terrestrial Ecosystem Science (TES) program, which examines the impact of climate change on biological systems and land-surface carbon cycle feedbacks to climate change.
$627 million taken from a taxpayer or borrowed from a future taxpayer, spent in one year. Next the Department of the Interior:
Department of the Interior (DOI).
DOI requests $171 million (an increase of 26.0 percent) for its Climate Change Adaptation initiative, which seeks to identify areas and species most vulnerable to climate change and implement coping strategies. Of this, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) would receive $77.9 million for climate science (an increase of 15.5 percent).
How many jobs could be created in 2011 if $171 million were still in the hands of US taxpayers, instead of being spent on climate studies which have been done many times before? Studying areas vulnerable to climate change? That’s already been done by every agency, twice. Next is the EPA:
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
EPA requests $169 million to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (an increase of 1 percent). Of this, $43.5 million is new funding for regulatory efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through the Clean Air Act. EPA requests $22 million for its Global Change Research Program, which assesses the impacts of global change on air and water quality, ecosystems, human health, and socioeconomic systems in the United States with a primary goal of promoting adaptation efforts.
I don’t even understand what this means. How does giving the EPA $169 million reduce emissions? Also, does it really cost $43.5 million a year (more) to regulate greenhouse gases? Lastly, the USDA:
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
USDA requests $159 million for climate change research, an increase of 42.0 percent, and $179 million for renewable energy, an increase of 41.0 percent. USDA’s climate change efforts (and those of the U.S. Forest Service which is part of USDA) center on helping farmers and land owners adapt to climate change impacts (e.g., enhanced fire stress, insect outbreaks, droughts, floods, and heat stress) and promoting carbon storage in soils and forests.
A 42% increase in climate change research? $159 million spent in a single year, by the USDA? Crop yields are up! CO2 helps crops! Imagine spending $159 million in 2011 to research things that actually help people.
The amount of money being spent on climate change research this year is astounding. I urge you to read the document yourself. Here is the question to take away: what are we getting for the billions of dollars we’ve spent? When 2011 is over will we look back at the published research and be satisfied with how our billions have been spent? This type of spending has occurred for some time, and what do we have to show for it? Multiple federal agencies having multi-hundred million dollar budgets in the same (controversial) field is wasteful. Let’s make sure 2011 is the last year these budgets increase.
See the analysis here.
Jan 07, 2011
Martinez axes all Environmental Improvement Board: Names Astronaut Schmitt to clean up policy
By Matthew Reichbach
Gov. Susana Martinez removed all the members of the state Environmental Improvement Board Tuesday for helping create an “anti-business environment.” Before being sworn in, Martinez was critical of the board’s decision to institute cap-and-trade rules in New Mexico.

Martinez wrote a letter to the members of the board informing them of her decision. She also said the members could apply for their old positions again and would consider their re-employment on a case by case basis.
In a stinging statement sent to the press, Martinez harshly criticized the members of the board.
“Unfortunately, the majority of EIB members have made it clear that they are more interested in advancing political ideology than implementing common-sense policies that balance economic growth with responsible stewardship in New Mexico,” Martinez wrote.
On her first day in office, Martinez had halted “all proposed and pending regulations,” which includes the cap-and-trade regulation. To rescind those rules, the new members of the EIB, which will be appointed by Martinez, will have to hold new public hearings and allow for public comment.
-------
Martinez picks former astronaut, global warming denier to head energy, natural resources department

Harrison Schmitt says government exerting pressure in climate science. Gov. Susana Martinez announced today that former astronaut and global warming denier Harrison Schmitt is her choice to run the Energy, Minerals and Natural Resources Department. A geologist and former senator, Schmitt would be in charge of the Mining and Minerals Division, State Parks Division, Oil Conservation Division and Energy Conservation Management Division if confirmed by the state Senate.
Schmitt, one of just 12 men to ever walk on the moon, was on Apollo 17, the final manned mission to the moon. He entered politics and served as U.S. Senator from 1977 to 1983. He was defeated by current U.S. Senator Jeff Bingaman in the 1982 election.
Schmitt does not believe global warming exists and says the government pressures scientists to support its existence. The vast majority of climate scientists agree that global warming is happening and say that humans are at least partially responsible. as do we, mainly through urbanization and land use changes
Schmitt has a doctorate in geology from Harvard University. Earlier this week, Martinez removed all the members of the Environmental Improvement Board, citing the board’s approval of regional and state cap and trade statutes. Read more here.
Let’s hope this starts a chain reaction in other states and in DC to undo the terrible harm done by the enviros.
Jan 06, 2011
Destroying the Credibility of Science
By Alan Caruba
Back in 1990 when I founded The National Anxiety Center as a clearinghouse for information about “scare campaigns” designed to influence public opinion and policy, I was mainly concerned about the torrent of lies about global warming.
Their beginning is usually dated to an appearance by James E. Hansen before a congressional committee in 1988 in which he claimed that global warming would destroy the earth. To this day Hansen heads the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and has held that position since 1981. There is no rational reason why he continues to be employed by the U.S. government.
Global warming has been widely discredited thanks to the November 2009 release of thousands of emails between UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change “scientists” that revealed their collusion to rig the data that supported the fraud.
GLOBAL WARMING. Climate alarmists are already worrying that the public has grown so tired of their idiotic claims that huge blizzards are caused by “warming” they are beginning to pour money into the education of a new generation of “environmental journalists” to ensure that more such lies make it to the front page of your daily newspaper or via other media.
Meanwhile, billions of taxpayer’s dollars have been flushed down the federal government rat hole to fund “research” guaranteed to support the hoax. It gets worse. Despite the defeat of the Cap-and-Trade bill based on the Big Lie that carbon dioxide and other so-called greenhouse gases cause global warming, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is attempting an end-run around Congress to impose limits on the carbon dioxide emissions of utilities and every form of manufacturing and business in America.
The EPA is engaged in a perversion of science, but what else is new? Americans have been ill-served by the alphabet soup of government agencies supposedly in place to protect the food we eat, medicines we take, the air and the water. In the process they are just as often stripping Americans of the protection afforded by pharmaceuticals and beneficial chemicals.
VACCINES v. AUTISM. A case in point is an article in the British Medical Journal that “accused a disgraced British doctor of committing an ‘elaborate fraud’ by faking data in his studies linking vaccines with autism.”
The result of that fraud was to convince thousands, if not millions, of parents that vaccines to protect their children against measles and mumps were a threat to their health. The ancillary question is why Andrew Wakefield’s paper was published in 1998. Science journals are expected to peer review such papers and determine if the data presented is valid. If it cannot be reproduced, it fails that test.
DDT. Starting in 1972, an EPA ban essentially ended its use anywhere in the nation and other nations followed suit. A year later a court upheld the EPA and that is an object lesson in what happens when matters of science are decided by men and women, lawyers, with no training or background in science. The DDT hoax continues to cause malaria deaths, particularly in Africa and mostly affecting women and children.
The U.S. is experiencing an outbreak of the bed bug population, eliminated decades ago, because the EPA has banned or limited the use of virtually every pesticide to exterminate them.
ALAR. Recall, too, the fraud perpetrated by environmental groups against Alar, a chemical that was widely used by apple growers to ensure that the crop would ripen in a fashion that permitted an efficient harvest. The Alar hoax cost American apple growers millions in lost revenue until it became known that Alar posed no health threat whatever.
SACCHARINE. Though cleared of charges dating from the 1980s that saccharin was a cancer-causing substance, it took until the 1990s to get it removed from the 9th edition of the “Report on Carcinogens” and it took until mid-December 2010 for the EPA to finally admit what everyone knew by then. You can thank “consumer” groups for foisting this fraud on everyone and agencies of the U.S. government for maintaining it until they no longer could.
BPA. A similar campaign exists to ban BPA, bisphenol-A, a chemical used to line plastic bottles and containers. It is literally a worldwide effort and it too is without any scientific merit. In the same way the claim that linked vaccines and autism, BPA is under attack, particularly in the U.S. and Europe. I have written about this in the past and intend to follow this to demonstrate how these “scientific” frauds debase all science in the process.
Aside from the fact that these claims always begin with a dubious “scientific” study and then escalate as other “scientists” climb on the funding bandwagon, the other element is always the role that the mainstream media plays in keeping the fraud alive until the sheer weight of evidence makes it impossible to do so.
Ultimately, this destroys the trust we normally accord to legitimate scientists, exhausting our ability and willingness to embrace the science that has prolonged and protected the lives of millions. Read more here.
Jan 04, 2011
Why Most Published Research Findings are False
By Dr. Roy Spencer
Those aren’t my words - it’s the title of a 2005 article, brought to my attention by Cal Beisner, which uses probability theory to “prove” that “...most claimed research findings are false”. While the article comes from the medical research field, it is sufficiently general that some of what it discusses can be applied to global warming research as well.
I would argue that the situation is even worse for what I consider to the central theory of the climate change debate: that adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere causes significant warming of the climate system. Two corollaries of that theory are that (1) the warming we have seen in recent decades is human-caused, and (2) significant warming will continue into the future as we keep using fossil fuels.
The first problem I see with scientifically determining whether the theory of anthropogenic global warming (AGW) is likely to be true is that it is a one-of-a-kind event. This immediately reduces our scientific confidence in pinpointing the cause of warming. The following proxy reconstruction of temperature variations over the last 2,000 years suggests global warming (and cooling), are the rule, not the exception, and so greenhouse gas increases in the last 100 years occurring during warming might be largely a coincidence.
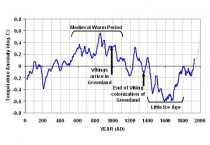
Enlarged here.
Twice I have testified in congress that unbiased funding on the subject of the causes of warming would be much closer to a reality if 50% of that money was devoted to finding natural reasons for climate change. Currently, that kind of research is almost non-existent.
A second, related problem is that we cannot put the Earth in the laboratory to run controlled experiments on. Now, we CAN determine in the laboratory that certain atmospheric constituents (water vapor, water droplets, carbon dioxide, methane) absorb and emit infrared energy...the physical basis for the so-called greenhouse effect. But the ultimate uncertainty over atmospheric feedbacks - e.g. determining whether cloud changes with warming reduce or amplify that warming - cannot be tested with any controlled experiment.
A third problem is the difficulty in separating cause from effect. Determining whether atmospheric feedbacks are positive or negative requires analysis of entire, quasi-global atmospheric circulation systems. Just noticing that more clouds tend to form over warm regions does not tell you anything useful about whether cloud feedbacks are positive or negative. Atmospheric and oceanic circulation systems involve all kinds of interrelated processes in which cause and effect must surely be operating. But separating cause from effect is something else entirely.
For example, just establishing that years experiencing global warmth have less cloud cover letting more sunlight in does not prove positive cloud feedback…simply because the warming could have been the result of - rather than the cause of - fewer clouds. This is the subject that Andy Dessler and I have been debating recently, and I consider it to be the Achilles heel of AGW theory.
After all, it is not the average role of clouds in the climate system that is being debated - we already know it is a cooling effect. It’s instead how clouds will change as a result of warming that we are interested in. Maybe they are the same thing (which is what I’m betting)...but so far, no one has found a way to prove or disprove it. And I believe cause-versus-effect is at the heart of that uncertainty.
A fourth problem with determining whether AGW theory is true or not is closely related to a similar problem medical research has - the source of funding. This has got to be one of the least appreciated sources of bias in global warming research. In pharmaceutical research, experimentally demonstrating the efficacy of some new drug might be influenced by the fact that the money for the research came from the company that developed the drug in the first place. This is partly why double-blind studies involving many participants (we have only one: Earth) were developed.
But in global warming research, there is a popular misconception that oil industry-funded climate research actually exists, and has skewed the science. I can’t think of a single scientific study that has been funded by an oil or coal company.
But what DOES exist is a large organization that has a virtual monopoly on global warming research in the U.S., and that has a vested interest in AGW theory being true: the U.S. Government. The idea that government-funded climate research is unbiased is laughable. The push for ever increasing levels of government regulation and legislation, the desire of government managers to grow their programs, the dependence of congressional funding of a problem on the existence of a “problem” to begin with, and the U.N.’s desire to find reasons to move toward global governance, all lead to inherent bias in climate research.
At least with medical research, there will always be funding because disease will always exist. But human-caused warming could end up to be little more than a false alarm...as well as a black eye for the climate research community. And lest we forget, possibly the biggest funding-related source of bias in climate research is that research community of scientists. Everyone knows that if the AGW “problem” is no longer a problem, their source of research funding will disappear.
Sometimes I get accused of being a conspiracy nut for believing these things. Well, whoever accuses me of that has obviously not worked in government or spent much time dealing with program managers in Washington. There is no conspiracy, because these things are not done in secret. The U.N.’s Agenda 21 is there for all to read.
The bottom line is that there could scarcely be a more ill-posed scientific question than whether global warming is human-caused: a one of a kind event, the Earth can’t be put into a laboratory to study, cause and effect are intermingled, and the political and financial sources of bias in the resulting research are everywhere.
So, when some scientist says we “know” that warming is human-caused, I cringe at the embarrassing abundance of scientific ignorance on display. No wonder the public doesn’t trust scientific predictions - just as suggested by the 2005 study I mentioned at the outset, those predictions have almost always been wrong!
Jan 03, 2011
Thick Ice Returns to Sea of Okhotsk and Traps 500 in Russian Ships
By Richard on Eureferendum
With Russian ships still trapped in the Sea of Okhotsk, in ice of two-metre thickness, Republican American blogger Steve Macoy recalls a 2006 symposium on global warming.
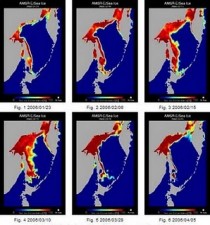
Illustrated were findings that that a large warming area existed in the western part of the Sea of Okhotsk, and a warming trend widely extended toward the western North Pacific. It was thus “widely believed” that the global warming was recently proceeding and the East Siberia region just north of the Sea of Okhotsk was one of the most sensitive areas to the global warming in the Northern Hemisphere.
The Sea of Okhotsk turns out to be quite an important area from the warmist perspective, this paper reporting that it plays a role as the pump of the North Pacific - thus having a significant effect on the climate of the region. It forms a significant ice factory for the whole region and there are said to be ”clear indications of global warming” around the sea.
This report in 2006 claimed a dramatic shrinkage of ice (illustrated), and a shortening ice season - with dire economic consequences. And it was this paper which reported on the area of the sea being “a sensitive area to the current global warming”, despite cyclical effects being reported elsewhere.
With the region now experiencing thick - and evidently unexpected [ ice, this is clearly of more importance than just the trapping of a number of ships. The ice in the whole region is something of a warmist poster child, and another one that has suddenly lost its appeal.
As the reducing ice extent has been used as evidence of global warming, so can we assume that the rapid increase in ice may be an early sign that the warming is over?
See post here.
---------
500 seamen stranded in icebound Russian ships
MOSCOW – A Russian icebreaker labored Monday through howling winds and heavy snow as it tried to reach icebound ships in the Sea of Okhotsk where more than 500 seamen are trapped.
Three of the vessels have been trapped since Friday in ice estimated to be two meters (6 1/2 feet) thick. The state news agency RIA Novosti said two more ships became stuck on Monday.
The Sea of Okhotsk is an arm of the northern Pacific to the west of Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula.
A statement from the Transport Ministry said there was no immediate danger to the crew on the three ships stuck since last week, who have sufficient food and water. The Ministry said an icebreaker was expected to reach their vicinity early Tuesday.
RIA Novosti cited a local coast guard official as saying winds on the sea were up to 30 meters per second (more than 65 mph).
The three ships that have been trapped since Friday - a fishing vessel, a refrigerated freighter and a scientific research ship - are in a tight convoy. The two others are about 20 nautical miles (35 kilometers) away.
See post here.
|







