Feb 25, 2009
Disappearing Arctic Ice Is Latest Climate Falsehood
By Doug L. Hoffman
In May, 2008, the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) predicted that the North Pole could be ice free during last years melt season.

The disappearing northern sea ice has been pointed to by global warming alarmists as visible proof that the Earth was doing a melt down. However, the NSIDC announced that they have been the victims of “sensor drift” that caused them to underestimate the Arctic ice extent this winter by as much as 500,000 square kilometers. It turns out that the demise of the arctic ice was greatly exaggerated.
As with the NASA Russian temperature debacle last year and the forced recalculation of US surface temperatures for the last century in 2007, the latest problem was discovered after NSIDC received emails from puzzled readers, asking why obviously sea-ice-covered regions were showing up as ice free open ocean. A statement on the NSIDC web site, published February 18, 2009, explains the current faux pas this way:
“As some of our readers have already noticed, there was a significant problem with the daily sea ice data images on February 16. The problem arose from a malfunction of the satellite sensor we use for our daily sea ice products. Upon further investigation, we discovered that starting around early January, an error known as sensor drift caused a slowly growing underestimation of Arctic sea ice extent. The underestimation reached approximately 500,000 square kilometers (193,000 square miles) by mid-February. Sensor drift, although infrequent, does occasionally occur and it is one of the things that we account for during quality control measures prior to archiving the data.”
The problem stemmed from a failure of the sea ice algorithm caused by degradation of one of the sensor channels on the DMSP F15 satellite. Upon further investigation, it was found that data quality had begun to degrade over the month preceding the catastrophic sensor failure. The NSIDC relies on an older, less-reliable method of tracking sea ice extent called SSM/I that does not agree with a newer method called AMSR-E. A comparison of the sensor drift can be seen in the accompanying chart (supersized here).
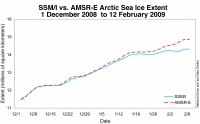
This error does not signal a change in the overall trend of sea ice reduction over the past several decades. Rather, it speaks to an all to common occurrence in the climate change debate - scientists getting caught basing dire predictions on bad data. This highlights the danger in accepting the at face value the often heard dismissal of anti-global warming arguments because the authors are not “real climate scientists.” Given the frequency of this type of data problem, we are forced to conclude that many climate scientists are really poor scientists, rushing to publish results that reinforce their own bias without ensuring the integrity of those results.
Once again we have misleading climate change pronouncements being based on data errors, data errors detected by non-UN, non-IPCC, non-peer-reviewed external observers. Sometimes it is the scientists themselves who discover the errors, as with the non-disappearing ice sheets of Greenland. More often than not, it is outside observers uncovering the errors, casting doubt on the trustworthiness of all science. This is exactly what happens when you base your arguments on “consensus science” and not scientific fact. What is happening to the Arctic ice this year? So far, the sea ice extent is tracking ahead of 2005, 2006, 2007, and 2008, so the predictions of an ice-free north pole might be a bit premature.

Professor Dr. Doug L. Hoffman, mathematician, computer programmer, and engineer, worked on environmental models and conducted research in molecular dynamics simulations and continues to teach at Hendrix College and the University of Central Arkansas. Hoffman co-authored a 2009 book The Resilient Earth, which touts itself as “bringing a dose of skeptical reality to climate science and the global warming debate.”
Feb 24, 2009
Alarmists Go after George Will and Washington Post for Daring to Question AGW
Global Warming Hoax
The left believes they’ve caught one of their arch enemies in a gross factual mistake. Nationally syndicated columnist George Will recently wrote that global sea ice was at the exact same levels as it was in 1979. The left went bonkers believing him to be incorrect. Was he? Discover Magazine’s blog is one of those that went off on George Will accusing him of gross inaccuracy and saying that the Washington Post had poor fact checking ”You Call That Fact-Checking?”.

Even the University of Illinois’ Arctic Climate Research Center got in to the fray saying this on their website: “We do not know where George Will is getting his information, but our data shows that on February 15, 1979, global sea ice area was 16.79 million sq. km and on February 15, 2009, global sea ice area was 15.45 million sq. km. Therefore, global sea ice levels are 1.34 million sq. km less in February 2009 than in February 1979. This decrease in sea ice area is roughly equal to the area of Texas, California, and Oklahoma combined.”
So was George Will wrong? It turns out George Will was quoting a source that later corrected its data, not George’s fault. Turns out for that particular day in February 1979 it did indeed have more ice than on that day in 2009. But is that a big deal?
We decided to take a look at the total month end numbers for January 1980 and January 2009. In case you’ve noticed a little slight of hand we did indeed change the year to one year later. Let it show that we did this to prove that it you can use this data just about any way you want (because frankly any global changes are not very dramatic), and if we had satellites up back in the 1930’s we probably would have seen far less sea ice than what we’re looking at now. So how does today compare to 1980?
1980 Southern Hemisphere = 4.7 million sq km
1980 Northern Hemisphere = 15.0 million sq km
Total = 19.7 million sq km
2009 Southern Hemisphere = 5.8 million sq km
2009 Northern Hemisphere = 14.1 million sq km
Total = 19.9 million sq km
January in the year 2009 showed 200,000 sq km more sea ice than 1980. So what did George Will say? “As global levels of sea ice declined last year, many experts said this was evidence of man-made global warming. Since September, however, the increase in sea ice has been the fastest change, either up or down, since 1979, when satellite record-keeping began. According to the University of Illinois’ Arctic Climate Research Center, global sea ice levels now equal those of 1979.” George Will’s point remains, there is as much sea ice today as there was in 1980. If there is “global” warming it certainly is hiding very well. Perhaps it has gone underground, either shy of all of the media attention, or nervous about being found out that it’s nothing more than a fraud.
Read more here. Looks like Discover needs to work on its fact checking. See this link that supports George Will’s right to present the science as he sees it much as Andy Revkin or Seth Borenstein is permitted to do here.
Feb 24, 2009
Northern Lights are Quietest in Decades
By Tim Mowry, Newsminer
FAIRBANKS: Ester photographer LeRoy Zimmerman made the switch to digital cameras this year to better capture the phenomenon known as the aurora borealis. Now he just needs some aurora to work with. “There’s nothing; it’s really disappointing,” Zimmerman said. “I’ve got my digital camera. I’m ready. Let’s go.”

AP photo of the aurora on February 29, 2008 near Palmer AK in the Newsminer story.
Zimmerman isn’t the only one wondering where the aurora borealis, commonly referred to as northern lights, are this winter. The Interior’s normal wintertime light show has been noticeably absent this winter. “I talk to people in town and everybody who knows what I do asks me, ‘Where is the aurora? What’s happening?’” said Dirk Lummerzheim, a research professor who studies the aurora borealis for the Geophysical Institute at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. It’s a legitimate question, and Lummerzheim has the answer. “We are at the solar minimum,” the UAF professor said. “When solar activity dies down like this, the aurora activity also diminishes in the north.”
Aurora borealis, a curtain-like, luminous glow in the upper atmosphere, is caused when energy particles from the sun collide with the Earth’s magnetic field. Solar activity runs on a 22-year cycle - 11 positive years and 11 negative years. The cycle is at the bottom of the negative cycle, Lummerzheim said. This is the second winter in a row the aurora has been “quiet,” as Lummerzheim put it. Normally, the low in the solar cycle only lasts about a year, he said. Lummerzheim described the current solar minimum as “very long, very deep.” “I think the last time we had a minimum this low was early in the 20th century,” he said. “If you look at the sun, I think we’ve had one sunspot group this year,” Lummerzheim said. “When we get into the maximum phase, it has lots of sunspots and all kinds of things going on all the time. There are big explosions.”
Aurora scholar Neal Brown, who directs UAF’s Alaska Space Grant Program, said the low in the current solar cycle is the most dramatic he has witnessed during his time in Fairbanks. “I’ve lived here for 45 years, and we’ve had four solar cycles, and this is the worst one for me,” Brown said. “It’s just been pitiful. I don’t think there’s been three or maybe four half-hour to hour-long displays this winter.”
The lack of an aurora has not been lost on businesses that cater to aurora viewers, specifically the hundreds of Japanese tourists who flock to Alaska each winter on direct flights from Japan to see the northern lights. “It hasn’t been as good a year as usual,” said Jenny Kirsch, assistant general manager at Chena Hot Springs Resort, a popular aurora viewing spot for many of the tourists. “Colors are hard to find.” Mok Kumagai at Aurora Borealis Lodge on Cleary Summit agreed. The aurora displays during the past two winters have been weak, he said.
“The impressive aurora hasn’t been as frequent,” Kumagai said. While he has been able to snap some decent pictures of the aurora, Kumagai noted that a camera tends to enhance what the naked eye sees, making the aurora more colorful and pronounced.
“Some of the days we’re getting photos, and it’s nice through the camera, but with the naked eye you can barely see it,” he said. Read full story here. More empirical evidence this solar cycle is extraordinary and a throwback in time to a quieter sun, cooler temperature era.
Feb 23, 2009
Blue Hill Observatory, MA: January Was in Some Ways Extraordinary
Blue Hill Observatory Newsletter Item

Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory, located at the top of a scenic mountain range south of Boston at an elevation of 635 feet, is a unique American institution. Founded in 1885 by Abbott Lawrence Rotch as a private scientific center for the study and measurement of the atmosphere, it was the site of many pioneering weather experiments and discoveries. The earliest kite soundings of the atmosphere in North America in the 1890s and the development of the radiosonde in the 1930s occurred at this historic site. It is home to the longest continuous history of weather observations in the United States. By combining data from nearby Milton and Canton, adjusted to Blue Hill, the data stretches back to 1831.
Today, the Observatory is a National Historic Landmark and remains committed to continuing its extensive, uninterrupted climate record with traditional methods and instruments. The recently established Science Center expands this mission by enhancing public understanding of atmospheric science. We are grateful for the generous support of members, friends, and corporations who make it possible to continue our benchmark climate observations and educational outreach programs. Please contact Charles Orloff by phone: (508) 776-1879 or email if you would like to make a donation to the Observatory. Sign up for our regular emails here. See our data here.
January 2009 Temperature & Wind; December-January snowfall
TEMPERATURE
The temperature in January never made it above 39 degrees, which is a new record for the lowest Monthly Maximum Temperature on record for the month of January.
January Coldest Maximum Temperature (deg F)
1) 39 in 2009
2) 40 in 2003
3) 41 in 1896
41 in 1948
5) 42 in 1925
42 in 1941
42 in 1985
The average monthly temperature of 21.8 degrees was about 25th coldest on record and only coldest since 2004.
Coldest January average temperatures (deg F)
Jan. 1920....15.5
Jan. 1888....16.3
Jan. 2004....17.2
WIND
The average corrected monthly mean wind speed of 13.1 MPH was the second lowest for any January on record checked back to 1885.
January Lowest Wind Speed (MPH)
1) 12.2 in 2001
2) 13.1 in 2009
3) 13.3 in 1984
4) 13.4 in 2005
5) 13.9 in 2008
The peak gust of 48 MPH is second lowest on records for January checked back to 1965 (behind 43 MPH in 2001). Prevailing wind direction from west at 36% is an unusually high percentage.
SNOWFALL
The December-January snowfall total of 55.1 inches is the 7th greatest on record.
Dec-Jan Highest Snowfall (inches)
1) 95.8 in 1947-48 [136.0 seasonal total]
2) 72.9 in 1995-96 [144.4 seasonal total]
3) 67.8 in 1922-23 [102.5 seasonal total]
4) 62.0 in 1903-04 [103.4 seasonal total]
5) 61.0 in 2004-05 [119.4 seasonal total]
6) 57.1 in 1945-46 [91.2 seasonal total]
7) 55.1 in 2008-09
8) 49.6 in 1976-77 [81.2 seasonal total]
There were no new daily records in the month of January.
Feb 21, 2009
Sea Ice Sensor Degradation Hits Cryosphere Today
By Anthony Watts, Watts Up With That
You may recall that I posted about how the National Snow and Ice Data Center has an issue with the DMSP satellite sensor channel used to detect sea ice. Cryosphere Today is a few days behind in update compared to NSIDC, and here is what their imagery now looks like before and after:
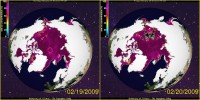
Here is the link to reproduce the image above.
Larger “holes” are likely to open up in the arctic sea in the next couple of days as the sensor further degrades.
Here is what CT has to say as a caveat for the side by side images:
February 17, 2009 - The SSMI sensor seems to be acting up and dropping data swaths from time to time in recent days. Missing swaths will appear on these images as a missing data in the southern latitudes. If this persists for more than a few weeks, we will start to fill in these missing data swaths with the ice concentration from the previous day. Note - these missing swaths do not affect the timeseries or any other plots on the Cryosphere Today as they are comprised of moving averages of at least three days.
No mention of the issue on CT’s main page though. They are still commenting on George Will. They seem a bit out of touch on the sensor issue.
h/t to Garrett
UPDATE: 11:30PM 2/20 CT has removed the comments about George Will from the main page, but still no mention there of the satellite outage nor are they displaying imagery on the main page from 2/20/09 The most recent is 02/19/09. It will be interesting to see what tomorrow brings. See Anthony’s post and comments here.
Icecap Note: the AMSR_E still is providing the most accurate data. It shows the following (larger image here) with the value of 14,032,188 square kms as of February 20, 2009:

See their mapping of the ice here.
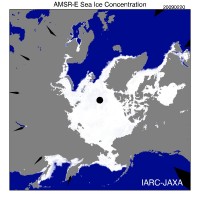
Anthony Watts also posted posted on this issue with a response from Dr. Walt Meier at NSIDC that the error related to satellite imaging dropout, mainly ice in Hudson Bay that went “missing” in the scan. Anthony explains why posting on these data discrepancy, questioned by Dr. Meier is valid.
See also NSIDC’s description of the problem, a failing satellite and why they chose to continue to use the older DMSP SSM/I data satellite data than to go to the newer more reliable and accurate satellite AMSR-E here.
|











