Dec 28, 2007
Weathering and Thermometer Shelters
By Anthony Watts
Patrick Michaels wrote in an American Spectator column today about the surface temperature record and this caught my eye: “Weather equipment is very high-maintenance. The standard temperature shelter is painted white. If the paint wears or discolors, the shelter absorbs more of the sun’s heat and the thermometer inside will read artificially high. But keeping temperature stations well painted probably isn’t the highest priority in a poor country.”
The Stevenson Screen experiment that I had setup this summer is living proof of this. Compare the photo of the whitewash paint screen on 7/13/07 when it was new with one taken today on 12/27/07. No wonder the NWS dumped whitewash as the spec in the 70’s in favor of latex paint. Notice that the Latex painted shelter still looks good today.

See full size images and more here in the Watts Up With That blog.
Anthony Watts is a former television meteorologist who operates a weather technology and content business. Weather measurement and presentation technology is his specialty. He has led a volunteer effort to document surface observing station siting at surfacestations.org
Dec 22, 2007
Exchange Between Roger Pielke Sr. and Andrew Revkin on Revkin’s Weblog “Climate Consensus Busted?”
By Roger Pielke Sr.
Read in the latest posting, the exchange between Andrew Revkin and Roger Pielke Sr. on the relative importance of the greenhouse gases in climate change.
Roger’s latest reply includes the following comments: However, as I read your reply, you are convinced that the climate will continue to warm from the greenhouse gases. Yet the lack of warming in recent years by several measures (upper ocean heat content, lower tropospheric temperatures), and the at best muted positive feedback from the water vapor feedback, indicates that we know quite a bit less on global warming than you indicate.
I agree the warming could resume (due to the diversity of positive climate forcings of which CO2 is up to 30% in a global average) but the lack of recent agreement between the models and the observations raises questions on whether negative feedbacks and negative climate forcings could actually result in cooling, at least for a period of time. After all the IPCC SPM admits that they left off climate forcings with a low level of scientific understanding.
With respect to added CO2, I am becoming convinced that its effect (threat?) is more from alterations in ocean and land biogeochemistry. rather than its radiative heating. I am also convinced (and have published on this as well) that the more heterogenous climate forcings (due to aerosols and land use/land cover) have a much greater impact on climate through alterations in atmospheric and ocean circulations than do the well-mixed greenhouse gases.
Dec 19, 2007
Year of Global Cooling
By David Deming, Commentary in the Washington Times
Al Gore says global warming is a planetary emergency. It is difficult to see how this can be so when record low temperatures are being set all over the world. In 2007, hundreds of people died, not from global warming, but from cold weather hazards.
Since the mid-19th century, the mean global temperature has increased by 0.7 degrees Celsius. This slight warming is not unusual, and lies well within the range of natural variation. Carbon dioxide continues to build in the atmosphere, but the mean planetary temperature hasn’t increased significantly for nearly nine years. Antarctica is getting colder. Neither the intensity nor the frequency of hurricanes has increased. The 2007 season was the third-quietest since 1966. In 2006 not a single hurricane made landfall in the U.S.
South America this year experienced one of its coldest winters in decades. In Buenos Aires, snow fell for the first time since the year 1918. Dozens of homeless people died from exposure. In Peru, 200 people died from the cold and thousands more became infected with respiratory diseases. Crops failed, livestock perished, and the Peruvian government declared a state of emergency.

Unexpected bitter cold swept the entire Southern Hemisphere in 2007. Johannesburg, South Africa, had the first significant snowfall in 26 years. Australia experienced the coldest June ever. In northeastern Australia, the city of Townsville underwent the longest period of continuously cold weather since 1941. In New Zealand, the weather turned so cold that vineyards were endangered. Read more about 2007 cold here.
David Deming is a geophysicist, an adjunct scholar with the National Center for Policy Analysis, and associate professor of Arts and Sciences at the University of Oklahoma.
Dec 18, 2007
Limits on Climate Sensitivity Derived from Recent Satellite and Surface Observations
By Petr Chylek, et.al. in the Journal of Geophysical Research
In a paper published December 2007 in the Journal of Geophysical Research, Petr Chylek et al found another source of model error when they found climate sensitivity is reduced by at least a factor of 2 when direct and indirect effects of decreasing aerosols are included. Their abstract:
An analysis of satellite and surface measurements of aerosol optical depth suggests that global average of aerosol optical depth has been recently decreasing at the rate of around 0.0014/a. This decrease is nonuniform with the fastest decrease observed over the United States and Europe. The observed rate of decreasing aerosol optical depth produces the top of the atmosphere radiative forcing that is comparable to forcing due to the current rate of increasing atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Consequently, both increasing atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases and decreasing loading of atmospheric aerosols are major contributors to the top-of-atmosphere radiative forcing. We find that the climate sensitivity is reduced by at least a factor of 2 when direct and indirect effects of decreasing aerosols are included, compared to the case where the radiative forcing is ascribed only to increases in atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide. We find the empirical climate sensitivity to be between 0.29 and 0.48 K/Wm−2 when aerosol direct and indirect radiative forcing is included.
Icecap Note: This amount is likely still an overestimate because of the assumption that all warming was due to radiative forcing, discounting natural factors, yet the conclusion undercuts the disaster scenarios. Put that together with lack of a long-term increase in precipitable water as noted by Pielke and found in Wang et.al., 2007 here and the oversimplified handling of the solar and oceans, and you can pretty much discard the climate models as an reliable tool for assessing future climate.
Dec 18, 2007
Antarctic Temperatures: 1958-2002
CO2 Science on Chapman and Walsh
Chapman and Walsh in “A synthesis of Antarctic Temperatures” in the Journal of Climate 2007, used monthly surface air temperatures from manned and automatic weather stations along with ship/buoy observations from the high-latitude Southern Hemisphere to develop a gridded database with resolution appropriate for applications ranging from spatial trend analyses to climate change impact assessments.
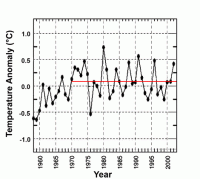
The data in the figure above clearly indicate a post-1958 warming of Antarctica and much of the surrounding Southern Ocean. From approximately 1970 to the end of the record, however, temperatures of the region simply fluctuated around an anomaly mean of about 0.12°C, neither warming nor cooling over the final 32 years of the record.
This latter observation is truly amazing in light of the fact that the region of study includes the Antarctic Peninsula, which experienced phenomenal warming during this period. Nevertheless, the mean surface air temperature of the entire region changed not at all, over a period of time that saw the air’s CO2 concentration rise by approximately 47 ppm (about 15% of its 1970 value, as per the Mauna Loa CO2 record).
Clearly, the entire continent of Antarctica, together with much of the Southern Ocean that surrounds it, has been completely oblivious to the supposedly “unprecedented” radiative impetus for warming produced by anthropogenic emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases over the last three decades of the 20th century ... and even a bit beyond. See more here.
|





